By Georgia (BA Archaeology, University of York)
I’m Georgia, an undergraduate student at the University of York, currently completing my dissertation on communicating archaeological techniques to children.

Back in December 2023 I welcomed a branch of the Young Archaeologists’ Club (YAC) to Avebury, to explore the henge, discover how the Avebury Papers team goes about transcribing diary entries, and explore the ways that archaeologists have historically made records.

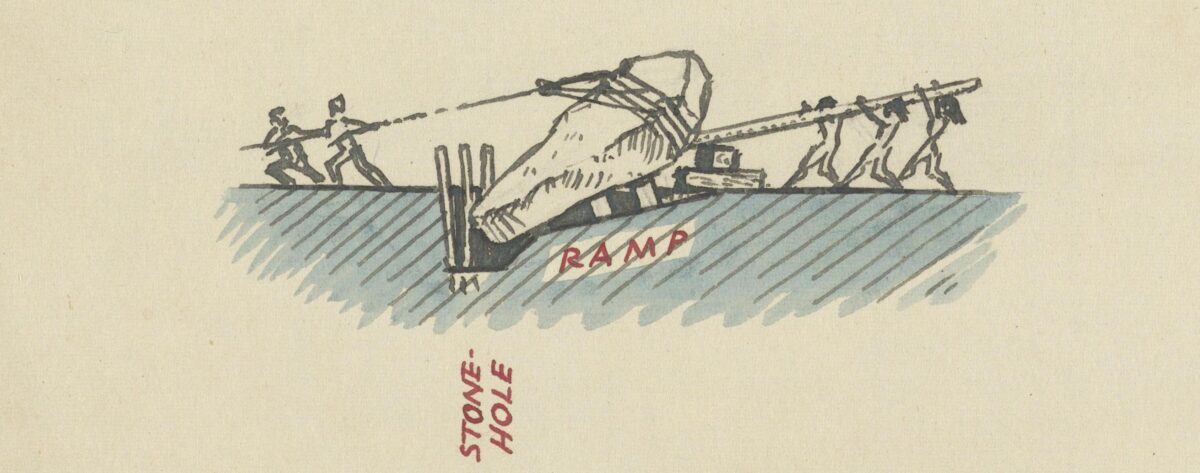
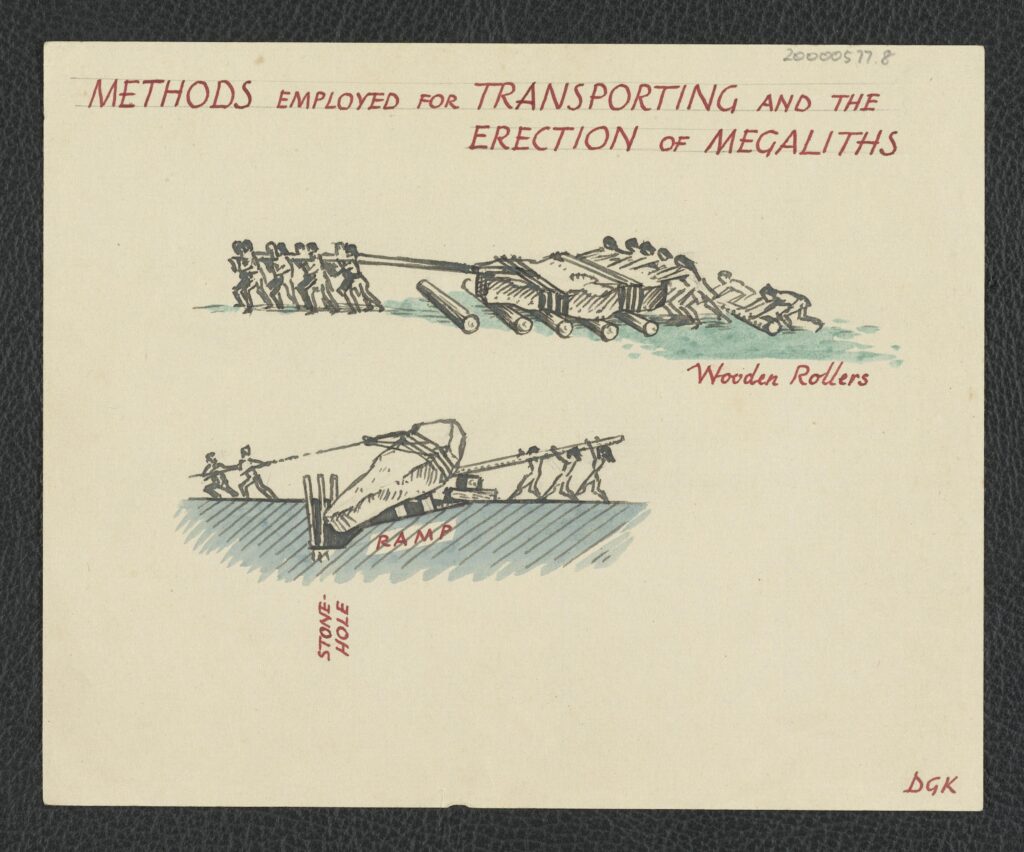
The session began with a short walk through the henge, where we talked about Keiller’s method of excavation and restoration at Avebury.
There were two activities, separated by a ten-minute break where the children had a snack and a drink. The first activity was based on transcription, where the children were given a range of extracts to try to detangle. The diary pages that were used in the session were taken from Denis Grant King’s 1938 account of his time at the site, as well as the 1934 excavation log written mostly by Alexander Keiller himself, with some entries penned by Stuart Piggott when he was absent.
These diaries represent a range from most complex handwriting (Keiller) to least difficult (Piggott). While I was researching and planning this session in August 2023, I visited the Avebury Papers volunteer team who were in the process of transcribing the excavation logs, which prompted conversation surrounding Alexander Keiller’s slightly illegible penmanship and inspired this activity.

As they had a go with transcription, a few of the kids asked about what the “answers” were for unfamiliar or indiscernible words. This began a discussion about what the Avebury Papers volunteers do when a word is unidentifiable, such as leaving a blank space or inserting their best guess between square brackets to show their uncertainty. Some of the children incorporated this methodology successfully into their own transcriptions.
The second activity asked the children to attempt to write their own diary entries, imagining that they had spent a day excavating on site.
The influence of the sources from the previous task was evident in some of the children’s diary entries. An example of this is in the picture below, in which it is clear that the child noticed and incorporated some of the style of Keiller’s excavation log, such as the abbreviation of names (e.g. Alexander Keiller becomes AK), the description of the weather, and his brief sentences. Although I’m glad they didn’t incorporate his indecipherable handwriting!

To end, I want to give a big thank you to the YAC members for being so enthusiastic, and to the YAC leaders for all their help throughout the planning process and the session itself.
You may freely view, download, and reuse the diary extracts (images and transcriptions) below. Right click to save images.
West Kennet Avenue 1934 excavation diary,
accession number 78510467
78510467: 19-20 April, written by Alexander Keiller, spread 71a-71b

*
78510467: 5-6 May, written by Alexander Keiller, spread 79a-79b

*
78510467: 2-3 August, written by Stuart Piggott, spreads 123-124


*
Denis Grant King, ‘Journal of my visit to Avebury:
Book Two’, accession number 1732623-002
Extract from 15 November 1938, spread 28